By Michael Poris, McIntosh Poris Architects Long defined by its industrial legacy, Detroit development currently combines ground-up construction with intelligent, innovative adaptive reuse. Brick-and-mortar manufacturing-era remnants include many buildings that originally served the automotive industry. As large-scale manufacturing relocated and Detroit’s population declined, several significant buildings were abandoned. Many are viable for second lives, ones that fulfill current commercial real estate market demands. Adaptive reuse makes sense I co-founded McIntosh Poris in 1994 to protect Detroit’s historic buildings from bulldozers and redesign them for a post-manufacturing economy. At that time, demolition was the most expedient option. To address this, we focused as much on civic networking and preservation education as architectural design. Implementation involved organizing events with public officials and the local business community to meet leaders of other cities’ successful urban-renewal programs. To make Detroit more attractive to commercial real estate investment, we lobbied for zoning changes. Most relevant, commercial and historic districts were re-evaluated to permit mixed-use redevelopment. Historic preservation became viable, often making sense both financially and culturally. Well before sustainability became a commercial real estate consideration, we educated developers on available adaptive reuse incentives such as historic tax credits. Combined with the inherent efficiencies of reuse, …
Market Reports
If there is one defining characteristic of the Raleigh-Durham retail market today, it is scarcity. Exceptionally low vacancy — especially in high-quality, well-located centers — has become the norm rather than the exception, fundamentally reshaping leasing dynamics, rent growth and development strategy across the region. As of third-quarter 2025, overall retail vacancy in Raleigh-Durham stood at approximately 2.4 percent, marking four consecutive years below the 3 percent threshold. Even more telling, spaces under 10,000 square feet posted vacancy closer to 1.8 percent, underscoring just how competitive conditions have become for local and regional tenants. This imbalance between demand and supply has placed landlords in a position of sustained leverage, particularly in grocery-anchored centers, strong neighborhood and lifestyle shopping centers or mixed-use environments. Low vacancy matters because it drives outcomes. Lease-ups are happening faster, concessions are increasingly rare in top trade areas and rents continue to trend upward. For tenants, especially those seeking smaller footprints, waiting to engage often means missing opportunities altogether. For owners, the market rewards proactive asset management and disciplined tenant selection. A clear example of this dynamic is Olde Raleigh Village, a grocery-anchored community shopping center that is currently 100 percent leased. With no vacancy to contend …
By Ryan Brittain, Colliers Speculative construction has always carried a certain boldness in industrial real estate. Building without a tenant can either signal visionary thinking or a bold bet on future demand. In metro Detroit, that confidence was on full display during the post-COVID boom. To meet the surge in tenant demand, highly respected industrial developers raced to deliver modern distribution space across the region. At the height, preleasing was not always necessary but often occurred. Developers pushed forward on new Class A warehouses, confident that tenant requirements would catch up and, for a time, they did. Yet here we are in 2026, and speculative development is not an idea of the past. It is returning, this time with more discipline. This is not another Resurgit cineribus Detroit comeback story, but rather a thoughtful recalibration. The “Return of the Spec” reflects a market that has matured and learned, not one that has overheated. To understand it today, it helps to revisit how we arrived. As a wave of newly completed speculative projects delivered (at one point, the market saw 12 million square feet under construction), availability expanded. Shortly thereafter, the automotive industry hit an uncertain patch in late 2023. Vacancy …
The Raleigh/Durham office market is not yet in full recovery mode; however, the latest data suggests something just as important: stabilization. Compared to many U.S. office markets still experiencing significant stress, Raleigh-Durham is holding its ground — and in several respects, outperforming national trends. Currently, the combined Raleigh-Durham office market totals approximately 118.7 million square feet, with Raleigh making up roughly two-thirds of the inventory and Durham the remainder. Together, they form one of the Southeast’s most dynamic and resilient office regions. Vacancy elevated, improving While higher than pre-pandemic norms, vacancy is trending better than many peer markets. Raleigh’s vacancy rate currently sits around 11.1 percent, while Durham’s vacancy rate is approximately 9.8 percent, according to research from CoStar Group. Combined, this market boasts a blended office vacancy rate of roughly 10.7 percent, well below the 14.1 percent national average. Over the past 12 months, Raleigh recorded positive net absorption of approximately 574,000 square feet, while Durham experienced negative absorption of about 480,000 square feet. Combined, the market landed near equilibrium, which sends an encouraging signal that the market is no longer sliding backward, even if growth remains uneven. The area’s post-pandemic growth is shaped by hybrid work models, changing …
By Joshua Allen and David Kelpe, JLL One year ago, CBRE Research forecasted a shortage of prime office space in Heartland Real Estate Business. That prediction has proven accurate. Since the beginning of 2025, demand for top-tier office space has continued to drive leasing activity across the region. This persistent appetite for quality has pushed prime Class A availability to record lows, creating a competitive environment for tenants and landlords alike. The St. Louis office market encompasses approximately 53 million square feet of competitive space. Yet, a closer look reveals a critical challenge: 73 percent of this inventory was constructed before the 1990s. This aging supply base means that only 2.6 million square feet qualifies as truly “prime” — the newest, most desirable assets located in walkable urban areas with abundant amenities. These buildings represent the gold standard for tenants seeking modern design, energy efficiency and proximity to vibrant neighborhoods. Currently, prime Class A availability sits at a mere 5.5 percent, a stark contrast to the 25.2 percent average for non-prime Class A assets. This gap reflects a clear and ongoing preference among tenants for buildings that combine high-quality construction with strategic location. In short, companies are willing to pay …
The Triangle’s industrial market continues to hold strong fundamentals heading into the new year. A disciplined construction pipeline, low vacancy and high absorption fuel the market’s steady success. Disciplined constructionIndustrial developers have been incredibly disciplined when delivering new product to the Raleigh-Durham market, which has kept vacancy below 7 percent — a significantly stronger rate than peer Sun Belt markets as a result of record levels of development in recent years. With absorption rates in the Triangle averaging nearly 3 million square feet per year in the past five years, this healthy rate of delivery and absorption has propped up the region’s industrial market. That being said, the Raleigh-Durham market infill land supply has its limitations. Industrial-zoned land is difficult to find and acquisition costs are pushing $500,000 per acre in some submarkets, and rezoning is a lengthy 12-month or longer process. For these projects to be financially viable, developers have been increasing rents year-over-year to an average of over $12 per square foot across all submarkets, up from roughly $6 just five years ago. Many institutional occupiers have been willing to pay a premium to be in new, Class A space in these infill areas, but other occupiers are …
By David Steinbach, JLL As artificial intelligence (AI) acceleration, cloud expansion and high-performance computing reshape the digital economy, cities across the U.S. are reevaluating whether they can meaningfully compete for data center investment. St. Louis is increasingly part of that national conversation — and the reasons are structural, not speculative. With competitive power pricing, repurposable industrial infrastructure, developable land and a strengthening policy framework, the region is positioned to capture the next wave of large-scale digital infrastructure. This moment represents more than a real estate opportunity. It’s an inflection point that could redefine the region’s industrial future if public and private stakeholders act in alignment. Cost, infrastructure profile Data center site selection begins with power and connectivity, and St. Louis offers meaningful advantages on both. Missouri’s industrial electricity rates continue to trend below the national average, with the state at 7.69 cents per kilowatt-hour compared with the U.S. industrial average of 8.65 cents per kilowatt-hour, according to the latest EIA data. This is a significant differentiator for large-scale campuses with substantial, long-duration energy needs. The region’s legacy industrial and former generation sites also come with high capacity transmission infrastructure that can be repurposed, reducing both development timelines and the cost …
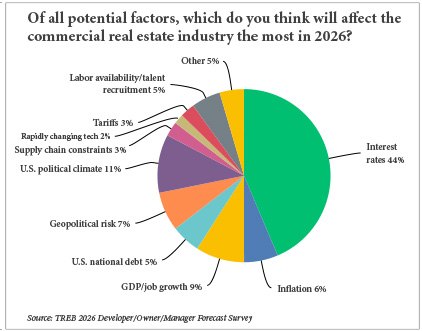
By Taylor Williams The results of Texas Real Estate Business’ annual reader forecast survey are in, and they paint a somewhat surprising picture of an optimistic business outlook for the new year. Why surprising? Well, geopolitically speaking, 2026 has already picked up right where 2025 left off. The Trump administration’s capture of Venezuelan president Nicolas Maduro and his wife in early January touched off a fresh source of geopolitical angst. The administration then subsequently ratcheted up its preexisting talk about Greenland becoming part of the United States, including issuing a threat to impose more tariffs on European countries that opposed that plan. Editor’s note: In mid-November, Texas Real Estate Business sent email invitations to participate in the annual online survey to three separate groups — brokers; developers, owners and managers; and lenders and financial intermediaries. The survey was held open through mid-December. Invitations to participate were also included in the Texas Real Estate Business e-newsletter, as well as through ReBusinessOnline.com. The tariff threat has since been walked back, but it’s hardly an understatement to say that the first month of 2026 has been rocky in terms of geopolitics. And when that happens, it’s anyone’s guess as to just how rattled markets …
After nearly three years of wrestling with oversupply, Raleigh-Durham’s multifamily market stands at an inflection point that informed investors have been quietly anticipating. The numbers tell a compelling story: construction starts plummeted from around 15,000 units in 2022 to roughly 2,000 in 2024, a staggering 86 percent decline that’s creating the supply drought the market desperately needed. The timing couldn’t be more critical. With an 18-month construction timeline followed by 12 to 16 months of lease-up process, the wave of deliveries from those record 2022 starts peaked in early-to-mid-2025. What comes next is perhaps the most interesting chapter in the Triangle’s multifamily story since our record rent jumps of 2021. Mathematics of recovery The construction cycle’s predictable timeline creates a unique visibility into market dynamics that astute capital allocators are already pricing in. The minimal 2024 starts are translating directly into minimal deliveries stretching from late 2025 through 2028 and beyond, which is essentially a three-year window of supply constraint that stands in stark contrast to the flood of new inventory and increased concessions that plagued 2023 to 2025. Meanwhile, demand fundamentals remain exceptionally strong. Gross absorption hit approximately 11,000 units in 2024 and is tracking toward another 10,000 (estimated) …
Port Authorities Advance the Southeast’s Industrial Sector With Infrastructural Investments
by John Nelson
In 2022, the Port of New Orleans (Port NOLA) announced the Louisiana International Terminal (LIT), a new $1.8 billion container terminal coming to Violet, a small city about 10 miles downriver (or south) from New Orleans in St. Bernard Parish. The project is a public-private partnership between Port NOLA and two private maritime industry leaders, Ports America and Terminal Investment Ltd., and is being funded with private capital and public funding from the State of Louisiana and federal sources. The U.S. Army Corps. of Engineers is managing LIT’s environmental review and permitting process, after which the public-private partnership will begin construction. Set for completion in 2028, the ambitious project is expected to generate 18,000 new jobs by 2050 and handle 2 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) of cargo traffic annually. “I consider it the most important project in the entire region,” says Andrew Marcus, founder of local commercial real estate services firm Agile Coast. “From an economic development perspective and from a quality-of-life perspective, it is the single-most important project for our region, period. The LIT is going to be the beachhead for getting modernized containerized cargo ships to come in, and we have the ability to have several terminals …
Newer Posts