“If you can make it in New York, you can make it anywhere.” Martin Scorsese, Frank Sinatra and Jay-Z probably weren’t thinking about brick-and-mortar retail real estate when they penned and recorded the iconic song lyric, but that doesn’t make the expression any less applicable to that particular subject. The notion of merchandisers, restaurateurs and entertainment operators needing a certain and precise combination of savvy, moxie and pizzazz to succeed in New York City isn’t so much new as it is resurrected. That’s because it’s only been a few years since the asset class was left for dead. But retail resiliency is now an established and proven narrative that underpins commercial real estate investment. “Brick-and-mortar retail is truly here to stay,” proclaims Beth Rosen, executive vice president at RIPCO Real Estate. “Over the years, retailers have gotten so much more savvy and are now entering into smarter deals. There’s a lot of positive sentiment about the sector, which has seen its share of ups and downs. Rents got really out of control at one point, and if the economy wasn’t strong, retailers didn’t survive. But now, it’s really more about partnerships between tenants and landlords.” Limited Options That said, owners …
Northeast Market Reports
By Joel Marcus, senior partner, Marcus & Pollack LLP COVID-19 and the government-ordered shutdown had immediate negative consequences for all types of real estate, and New York City’s tax valuations took this into account. Damage from the pandemic still weighs down property values today, compounded by cultural shifts that sapped demand for commercial properties. Fair market values have evolved to reflect pervasive vacancy, building obsolescence and the heightened cost of serving tenants that have abundant alternatives to choose from. At the same time, work-from-home practices reduce space requirements. Retailers, restaurants and hotels see half the foot traffic they once had from nearby office buildings, adding to ongoing pressure from e-commerce and other challenges to create excess vacancy, constrained rental streams and declining market values. Valuation for property taxation has not evolved, however, judging by the revaluation tax assessments the city’s Department of Finance is issuing. Revaluations ostensibly update taxable property values to current fair market value. Yet New York’s assessors habitually inflate valuations by applying pre-pandemic rental rates and vacancy assumptions, ignoring the rents landlords are actually collecting today and turning a blind eye to fundamental changes in demand for commercial space. Old thinking persists among these assessors, and it …
By Taylor Williams What do the phrases “owner-occupier,” “small-bay” and “mid-range WALT” have in common? They could potentially be obscure references to real-life inspirations behind songs on the new Taylor Swift album. But just in case that’s not the case, these terms also represent types of industrial investment plays that have become increasingly favorable among owners and prospective buyers in Northeast markets. The rising popularity of these deals attests to shifts in the broader landscape, i.e. — large-scale e-commerce and logistics facilities have been either overbuilt or priced to perfection in many areas. But the past 12 months have seen industrial deal volume in major Northeast markets regain traction. Although some — if not most — of that activity is tied to interest rates and geopolitics, the emergence of different deal types is nonetheless a positive indicator because it speaks to the creative approach that the investment community has taken in its return to the market. Unlike a few years ago, industrial real estate today is not a mindless beneficiary of both institutional and private debt and equity — a bottomless pit of capital flows. Tenants are no longer forced to write quasi-blank checks to owners just to secure crucial …
By Taylor Williams Retail and restaurant operators looking to enter or expand within the Philadelphia metro area are increasingly looking at suburban locations, and owners of those properties and seasoned brokers within the market both say there’s more to the trend than a simple lack of availability in key urban retail nodes. “The suburbs have been the preferred asset class — to some degree the first choice — for some retailers,” says Kari Glinski, vice president of asset management at regional owner-operator Federal Realty Investment Trust. “It started during COVID, when everybody was home, and with a lot of people living in the suburbs, we’ve seen strong demand. For well-located suburban properties, the leasing volume over the past three years has been at historical highs.” “Even over the past 12 to 24 months, supply has absolutely been constrained and should be even more constrained going forward,” Glinski continues. “For well-located properties backed by demand, new development can work. But right now, with where the cost of capital is, there’s not going to be a huge pop in new supply, thus creating a scarcity of well-located retail space.” Glinski acknowledges that since Federal Realty doesn’t operate many projects in the city, …
You can be a best-in-class operator with the coolest concept on the block, or you can be a well-capitalized landlord who knows all the right people, but if rapid, sustainable growth in the Boston retail market is what you seek, you might be SOL. According to local brokers, the high-demand, low-supply dynamic that currently exists in most major U.S. retail markets does not fully encapsulate the difficulties that tenants and landlords alike face in growing their footprints in the greater Boston area. As to why growing store counts or portfolios is so challenging in this market, the answer varies depending on who you ask. But a collective recap of all wide-ranging barriers to entry and disruptive forces at play paints a picture of a market that is borderline impenetrable for many tenants and perpetually stagnating for many landlords. “Boston remains an incredibly high-barrier-to-entry market,” says Zach Nitsche, director of retail capital markets in JLL’s Boston office. “A statistic we like to share with clients and industry people that haven’t historically invested in Boston and New England is that less than 5 percent of our total retail product has been constructed after the Global Financial Crisis. So far this year, the …
By Tom Kucharski, CEO of Invest Buffalo Niagara When Ralph Wilson selected Buffalo to be the home of the new Bills franchise in the American Football League in the 1950s, it was one of the nation’s 10 highest populated cities, making it a natural fit. However, a general shift around the country away from traditional manufacturing as a major base for economic activity, combined with a number of other factors, led to a decline in the city’s employment and population bases in the ensuing decades. Over the past 25 years, Buffalo has reversed that trend, emerging as a city on the rise. The region recently saw its first population growth in over 70 years, according to the 2020 census. That growth has been spurred by a diversification of the local economy, attracting businesses in industries such as advanced manufacturing, food processing and life sciences. Companies were especially enticed by the region’s low cost of doing business and affordable energy supplied by the nearby Niagara River. A key to maintaining that momentum has been Buffalo’s self-reinvestment, including massive redevelopment projects centered around reclaiming the city’s waterfront district. The first wave of these efforts began about a decade ago. Specifically, prior to …
By Wick Zimmerman, CEO of Outside the Lines Inc. In the Northeast’s evolving commercial real estate landscape, mall owners and operators are navigating now-familiar headwinds: changing consumer behaviors, declining legacy retail brands and the sustained presence of e-commerce. Yet amid these pressures, a reinvention is underway. Malls are shedding their images as static retail venues and transforming into immersive, tech-enabled destinations — and it’s not traditional retail driving the charge. It’s Gen Z, a digitally native, experience-driven cohort that’s redefining what mall real estate can and should be. This shift presents both a challenge and an opportunity for regional retail stakeholders. The challenge? Retrofitting aging assets to meet evolving demands. The opportunity? Creating diversified, high-traffic destinations that outperform their square footages in terms of both revenue and relevance. From Shopping Centers to Engagement Anchors Once emblematic of suburban retail, malls across the Northeast — from Long Island to greater Boston — are increasingly being reimagined as hybridized spaces that combine shopping, entertainment and community programming. In densely populated, high-barrier markets, where new development is constrained, adaptive reuse initiatives are driving the charge. Class B and C malls, in particular, are being repositioned with new anchors — not department stores, but …
By Taylor Williams The retail markets throughout the greater New York City area have been starving for more quality space in the post-pandemic era, with ground-up supply gains rarely hitting the market outside of obligatory inclusions within apartment buildings and highly curated clusters at mixed-use developments. According to JLL’s latest market report on New York City, as of the first quarter of 2025, there were approximately 200 availabilities across Manhattan’s “prime” retail submarkets — a record low. Average asking rents leapt 7.4 percent between the fourth quarter of 2024 and the ensuing period, settling at a rate of $577 per square foot. The report identified traditionally ritzy retail corridors and hotspots such as Fifth Avenue, Madison Avenue, SoHo and Times Square as recipients of the “prime” label, also designating the Williamsburg district in Brooklyn as one such area. So when well-located spaces formerly occupied by retailers that are now defunct or aggressively downsizing become available, they tend to draw major, immediate interest. “Expanding retailers have substantial opportunities to backfill big box and junior spaces vacated by bankrupt chains,” says Mitzi Flexer, managing director in the New York City office of national brokerage firm Bradford Allen. Flexer says that a notable …
By Taylor Williams So much for “survive ’til ’25.” Until a couple months ago, industrial owners in the markets of New Jersey and Eastern Pennsylvania had good reason to believe that 2025 would be a year in which ground-up development got back on track. And in those markets, which are defined by their density and sticky tenant demand, new supply is rarely a bad thing. According to the latest data available from Colliers, industrial vacancy rates in Philadelphia County, Southern New Jersey and the Lehigh Valley all rose in the fourth quarter by anywhere from 80 to 150 basis points. The regionwide vacancy rate stood at roughly 7 percent at the end of 2024, up from 6 percent in the fourth quarter of 2023. The Colliers report also noted that while more than 6 million square feet of predominantly speculative product came on line in the first quarter of 2025, subsequent deliveries were forecast to decline by 40 to 50 percent in each ensuing quarter, “signaling a slowdown in supply for the remainder of the year.” Demand in the region remains healthy but has undoubtedly moderated from record levels that prevailed several years ago, according to Scott Mertz, SIOR, president …
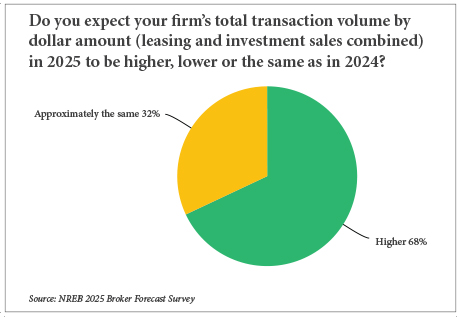
By Taylor Williams They may not be ready to do cartwheels and pop champagne, but when it comes to business expectations for 2025, commercial real estate professionals in the Northeast have a decidedly brighter outlook than in recent years. The last two years have been defined by barriers to economic growth on numerous levels. Pick your post-COVID geopolitical or macroeconomic poison — stubborn inflation, crushing interest rate hikes, multiple wars, restarting of global supply chains — all culminating with an incredibly heated U.S. presidential election. Is it any wonder that “survive till ’25” became the rallying cry of the commercial real estate industry? And while 2025 has arrived, the election has been decided and the Federal Reserve has strung together a series of small, yet meaningful cuts to short-term interest rates, the hangover from the aforementioned disruptors has not fully evaporated. Donald Trump’s return to the Oval Office brings a fresh slate of questions about how certain policies — namely tariffs and mass deportations — will impact business at both the national and local levels. And the expectation-smashing December jobs report proved sufficient to immediately pause the Fed’s would-be pattern of rate cuts. And it’s only been one month. As …
Newer Posts